In order to configure the ASA for VPN access using the AnyConnect client, complete these steps:
1. Configure a Self-Issued Certificate.
2. Upload and Identify the SSL VPN Client Image.
3. Enable Anyconnect Access.
4. Create a new Group Policy.
5. Configure Access List Bypass for VPN Connections.
6. Create a Connection Profile and Tunnel Group for the AnyConnect Client Connections.
7. Configure NAT Exemption for AnyConnect Clients.
8. Add Users to the Local Database.
Step 1. Configure a Self-Issued Certificate
By default, the security appliance has a self-signed certificate that is regenerated every time the device is rebooted. You can purchase your own certificate from vendors, such as Verisign or EnTrust, or you can configure the ASA to issue an identity certificate to itself. This certificate remains the same even when the device is rebooted. Complete this step in order to generate a self-issued certificate that persists when the device is rebooted.
ASDM Procedure
1. Click Configuration, and then click Remote Access VPN.
2. Expand Certificate Management, and then choose Identity Certificates.
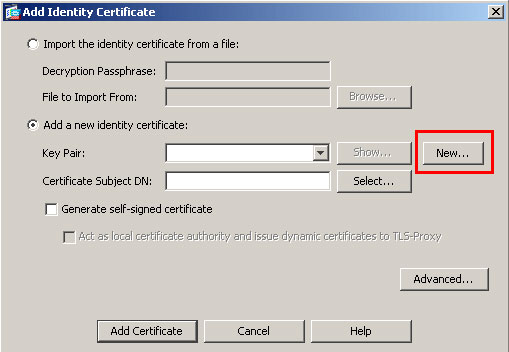
3. Click Add, and then click the Add a new identity certificate radio button.
4. Click New.
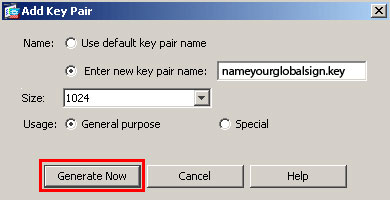
5. In the Add Key Pair dialog box, click the Enter new key pair name radio button.
6. Enter a name to identify the keypair.
This example uses sslvpnkeypair.
7. Click Generate Now.
8. In the Add Identity Certificate dialog box, ensure the newly created key pair is selected.
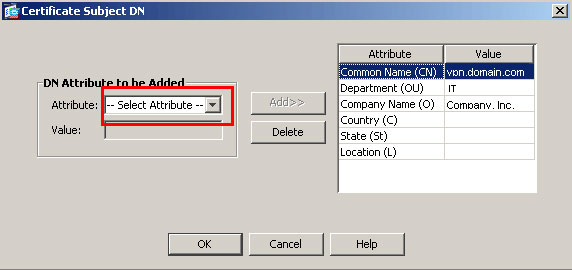
9. For Certificate Subject DN, enter the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) that will be used to connect to the VPN terminating interface.
CN=sslvpn.cisco.com
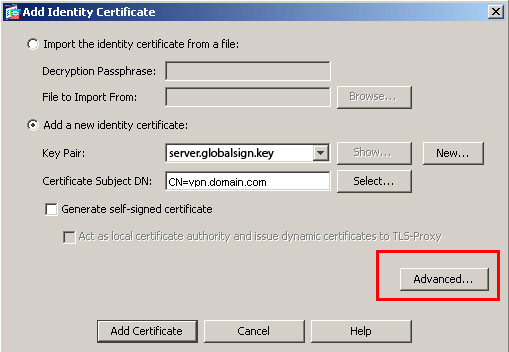
10. Click Advanced, and enter the FQDN used for the Certificate Subject DN field.
For example, FQDN: sslvpn.cisco.com
11. Click OK.
12. Check the Generate Self Signed Certificate check box, and click Add Certificate.
13. Click OK.
14. Click Configuration, and then click Remote Access VPN.
15. Expand Advanced, and choose SSL Settings.
16. In the Certificates area, choose the interface that will be used to terminate the SSL VPN (outside), and click Edit.
17. In the Certificate drop-down list, choose the self-signed certificate that you generated earlier.
18. Click OK, and then click Apply.
Command Line Example
| ciscoasa |
ciscoasa(config)#crypto key generate rsa label sslvpnkeypair INFO: The name for the keys will be: sslvpnkeypair Keypair generation process begin. Please wait... !--- Generate an RSA key for the certificate. (The name should be unique. !--- For example, sslvpnkeypair.) ciscoasa(config)#crypto ca trustpoint localtrust !--- Create a trustpoint for the self-issued certificate. ciscoasa(config-ca-trustpoint)#enrollment self ciscoasa(config-ca-trustpoint)#fqdn sslvpn.cisco.com ciscoasa(config-ca-trustpoint)#subject-name CN=sslvpn.cisco.com !--- The fully qualified domain name is used for both fqdn and CN. !--- The name should resolve to the ASA outside interface IP address. ciscoasa(config-ca-trustpoint)#keypair sslvpnkeypair !--- The RSA key is assigned to the trustpoint for certificate creation. ciscoasa(config-ca-trustpoint)#crypto ca enroll localtrust noconfirm % The fully-qualified domain name in the certificate will be: sslvpn.cisco.com ciscoasa(config)# ssl trust-point localtrust outside !--- Assign the trustpoint to be used for SSL connections on the outside interface. |
Step 2. Upload and Identify the SSL VPN Client Image
ASDM Procedure
1. Click Configuration, and then click Remote Access VPN.
2. Expand Network (Client) Access, and then expand Advanced.
3. Expand SSL VPN, and choose Client Settings.
4. In the SSL VPN Client Images area, click Add, and then click Upload.
5. Browse to the location where you downloaded the AnyConnect client.
6. Select the file, and click Upload File.
Once the client uploads, you receive a message that states the file was uploaded to flash successully.
7. Click OK.
A dialog box appears to confirm that you want to use the newly uploaded image as the current SSL VPN client image.
8. Click OK.
9. Click OK, and then click Apply.
10. Repeat the steps in this section for each operating system-specific Anyconnect package that you want to use.
Command Line Example
| ciscoasa |
ciscoasa(config)#copy tftp://192.168.50.5/anyconnect-win-2.0.0343-k9.pkg flash Address or name of remote host [192.168.50.5]? Source filename [anyconnect-win-2.0.0343-k9.pkg]? Destination filename [anyconnect-win-2.0.0343-k9.pkg]? Accessing tftp://192.168.50.5/anyconnect-win-2.0.0343-k9.pkg...!!!!!!!!!!!!! Writing file disk0:/anyconnect-win-2.0.0343-k9.pkg... !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! 2635734 bytes copied in 4.480 secs (658933 bytes/sec) !--- AnyConnect image is downloaded to ASA via TFTP. ciscoasa(config)#webvpn ciscoasa(config-webvpn)#svc image disk0:/anyconnect-win-2.0.0343-k9.pkg 1 !--- Specify the AnyConnect image to be downloaded by users. The image that is !--- downloaded the most should have the lowest number. This image uses 1 for the !--- AnyConnect Windows image. |
Step 3. Enable Anyconnect Access
ASDM Procedure
1. Click Configuration, and then click Remote Access VPN.
2. Expand Network (Client) Access, and then choose SSL VPN Connection Profiles.
3. Check the Enable Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client check box.
4. Check the Allow Access check box for the outside interface, and click Apply.
Command Line Example
| ciscoasa |
ciscoasa(config)#webvpn ciscoasa(config-webvpn)#enable outside ciscoasa(config-webvpn)#svc enable !--- Enable AnyConnect to be downloaded to remote computers. |
Step 4. Create a new Group Policy
A group policy specifies the configuration parameters that should be applied to clients when they connect. This example creates a group policy named SSLClientPolicy.
ASDM Procedure
1. Click Configuration, and then click Remote Access VPN.
2. Expand Network (Client) Access, and choose Group Policies.
3. Click Add.
4. Choose General, and enter SSLClientPolicy in the Name field.
5. Uncheck the Address Pools Inherit check box.
6. Click Select, and then click Add.
The Add IP Pool dialog box appears.
7. Configure the address pool from an IP range that is not currently in use on your network.
This example uses these values:
o Name: SSLClientPool
o Starting IP Address: 192.168.25.1
o Ending IP Address: 192.168.25.50
o Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
8. Click OK.
9. Choose the newly created pool, and click Assign.
10. Click OK, and then click More Options.
11. Uncheck the Tunneling Protocols Inherit check box.
12. Check SSL VPN Client.
13. In the left pane, choose Servers.
14. Uncheck the DNS Servers Inherit check box, and enter the IP address of the internal DNS server that the AnyConnect clients will use.
This example uses 192.168.50.5.
15. Click More Options.
16. Uncheck the Default Domain Inherit check box.
17. Enter the domain used by your internal network. For example, tsweb.local .
18. Click OK, and then click Apply.
Command Line Example
| ciscoasa |
ciscoasa(config)#ip local pool SSLClientPool 192.168.25.1-192.168.25.50 mask 255.255.255.0 !--- Define the IP pool. The IP pool should be a range of IP addresses !--- not already in use on the internal network. ciscoasa(config)#group-policy SSLCLientPolicy internal ciscoasa(config)#group-policy SSLCLientPolicy attributes ciscoasa(config-group-policy)#dns-server value 192.168.50.5 !--- Specify the internal DNS server to be used. ciscoasa(config-group-policy)#vpn-tunnel-protocol svc !--- Specify VPN tunnel protocol to be used by the Group Policy. ciscoasa(config-group-policy)#default-domain value tsweb.local !--- Define the default domain assigned to VPN users. ciscoasa(config-group-policy)#address-pools value SSLClientPool !--- Assign the IP pool created to the SSLClientPolicy group policy. |
Step 5: Configure Access List Bypass for VPN Connections
When you enable this option, you allow the SSL/IPsec clients to bypass the interface access list.
ASDM Procedure
1. Click Configuration, and then click Remote Access VPN.
2. Expand Network (Client) Access, and then expand Advanced.
3. Expand SSL VPN, and choose Bypass Interface Access List.
4. Ensure the Enable inbound SSL VPN and IPSEC Sessions to bypass interface access lists check box is checked, and click Apply.
Command Line Example
| ciscoasa |
ciscoasa(config)#sysopt connection permit-vpn !--- Enable interface access-list bypass for VPN connections. !--- This example uses the vpn-filter command for access control. ciscoasa(config-group-policy)# |
When VPN clients connect to the ASA, they connect to a connection profile or tunnel group. The tunnel group is used to define connection parameters for specific types of VPN connections, such as IPsec L2L, IPsec remote access, clientless SSL, and client SSL.
ASDM Procedure
1. Click Configuration, and then click Remote Access VPN.
2. Expand Network (Client) Access, and then expand SSL VPN.
3. Choose Connection Profiles, and click Add.
4. Choose Basic, and enter these values:
o Name: SSLClientProfile
o Authentication: LOCAL
o Default Group Policy: SSLClientPolicy
5. Ensure the SSL VPN Client Protocol check box is checked.
6. In the left pane, expand Advanced, and choose SSL VPN.
7. Under Connection Aliases, click Add, and enter a name to which users can associate their VPN connections. For example, SSLVPNClient.
8. Click OK, and then click OK again.
9. At the bottom of the ASDM window, check the Allow user to select connection, identified by alias in the table above at login page check box, and click Apply.
Command Line Example
| ciscoasa |
ciscoasa(config)#tunnel-group SSLClientProfile type remote-access !--- Define tunnel group to be used for VPN remote access connections. ciscoasa(config)#tunnel-group SSLClientProfile general-attributes ciscoasa(config-tunnel-general)#default-group-policy SSLCLientPolicy ciscoasa(config-tunnel-general)#tunnel-group SSLClientProfile webvpn-attributes ciscoasa(config-tunnel-webvpn)#group-alias SSLVPNClient enable !--- Assign alias for tunnel group. ciscoasa(config-tunnel-webvpn)#webvpn ciscoasa(config-webvpn)#tunnel-group-list enable !--- Enable alias/tunnel group selection for SSL VPN connections. |
Step 7. Configure NAT Exemption for AnyConnect Clients
NAT exemption should be configured for any IP addresses or ranges you want to allow the SSL VPN clients to access. In this example, the SSL VPN clients need access to the internal IP 192.168.50.5 only.
Note: If NAT-control is not enabled, this step is not required. Use the show run nat-control command to verify. In order to verify through ASDM, click Configuration, click Firewall, and choose Nat Rules. If the Enable traffic through the firewall without address translation check box is checked, you can skip this step.
ASDM Procedure
1. Click Configuration, and then click Firewall.
2. Choose Nat Rules, and click Add.
3. Choose Add NAT Exempt Rule, and enter these values:
o Action: Exempt
o Interface: inside
o Source: 192.168.50.5
o Destination: 192.168.25.0/24
o NAT Exempt Direction: NAT Exempt outbound traffic from interface 'inside' to lower security interfaces (Default)
4. Click OK, and then click Apply.
Command Line Example
| ciscoasa |
ciscoasa(config)#access-list no_nat extended permit ip host 192.168.50.5 192.168.25.0 255.255.255.0 !--- Define access list to be used for NAT exemption. ciscoasa(config)#nat (inside) 0 access-list no_nat !--- Allow external connections to untranslated internal !--- addresses defined by access lisy no_nat. ciscoasa(config)# |
If you use local authentication (the default), you must define user names and passwords in the local database for user authentication.
ASDM Procedure
1. Click Configuration, and then click Remote Access VPN.
2. Expand AAA Setup, and choose Local Users.
3. Click Add, and enter these values:
o Username: matthewp
o Password: p@ssw0rd
o Confirm Password: p@ssw0rd
4. Select the No ASDM, SSH, Telnet or Console Access radio button.
5. Click OK, and then click Apply.
6. Repeat this step for additional users, and then click Save.
Command Line Example
| ciscoasa |
ciscoasa(config)#username matthewp password p@ssw0rd ciscoasa(config)#username matthewp attributes ciscoasa(config-username)#service-type remote-access !--- Assign user remote access only. No SSH, Telnet, ASDM access allowed. ciscoasa(config-username)#write memory !--- Save the configuration. |
Use this section in order to verify that the SSL VPN configuration is successful
Connect to the ASA with the AnyConnect Client
Install the client directly on a PC, and connect to the ASA outside interface, or enter https and the FQDN/IP address of the ASA in a web browser. If you use a web browser, the client installs itself upon successful login.
Verify SSL VPN Client Connections
Use the show vpn-sessiondb svc command in order to verify connected SSL VPN clients.
ciscoasa(config-group-policy)#show vpn-sessiondb svc
Session Type: SVC
Username : matthewp Index : 6
Assigned IP : 192.168.25.1 Public IP : 172.18.12.111
Protocol : Clientless SSL-Tunnel DTLS-Tunnel
Encryption : RC4 AES128 Hashing : SHA1
Bytes Tx : 35466 Bytes Rx : 27543
Group Policy : SSLClientPolicy Tunnel Group : SSLClientProfile
Login Time : 20:06:59 UTC Tue Oct 16 2007
Duration : 0h:00m:12s
NAC Result : Unknown
VLAN Mapping : N/A VLAN : none
ciscoasa(config-group-policy)#
The vpn-sessiondb logoff name username command logs off users by user name. An Administrator Reset message is sent to the user when disconnected.
ciscoasa(config)#vpn-sessiondb logoff name matthewp
Do you want to logoff the VPN session(s)? [confirm]
INFO: Number of sessions with name "matthewp" logged off : 1